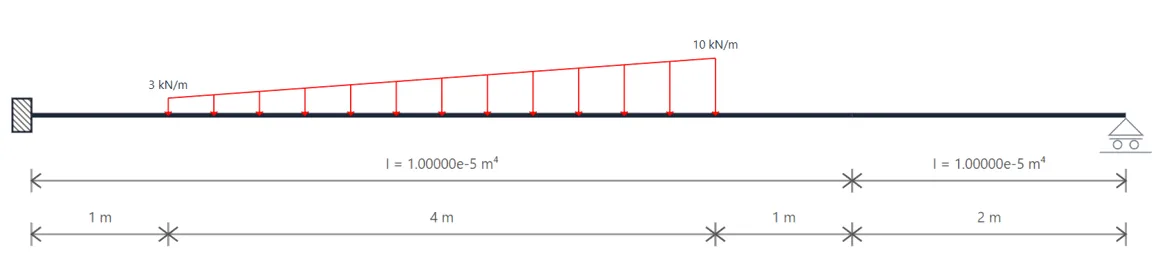
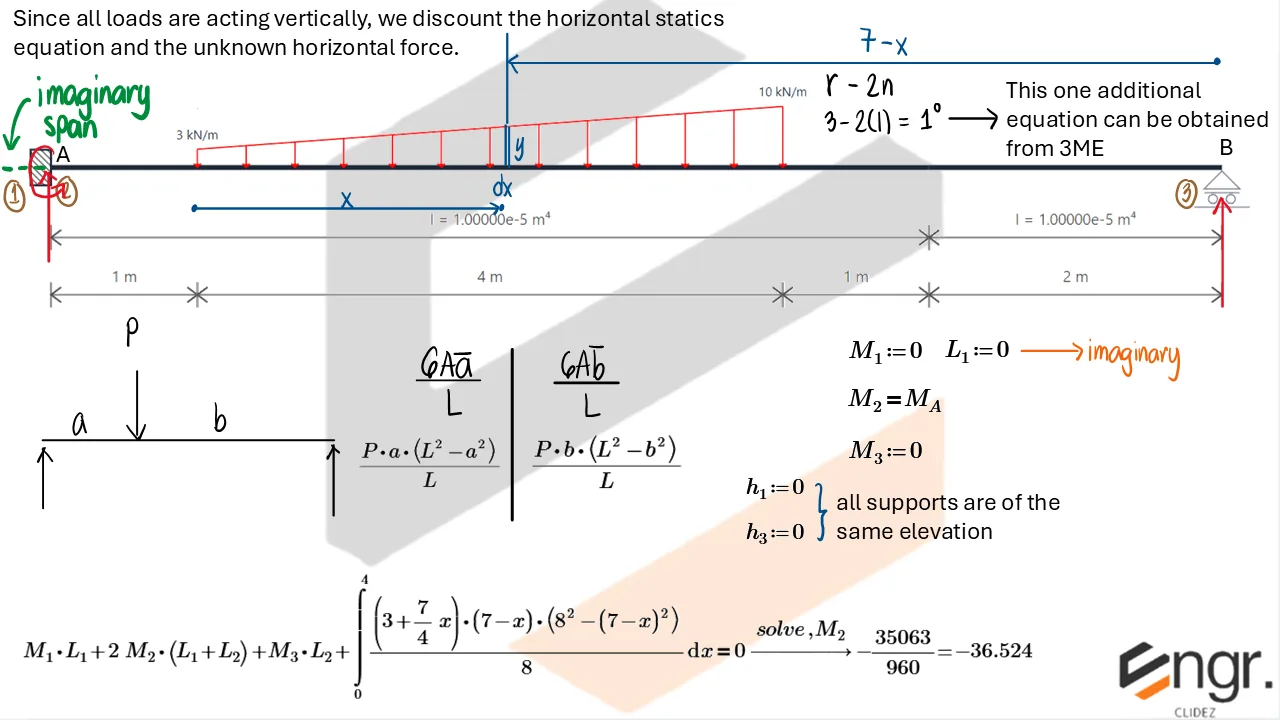
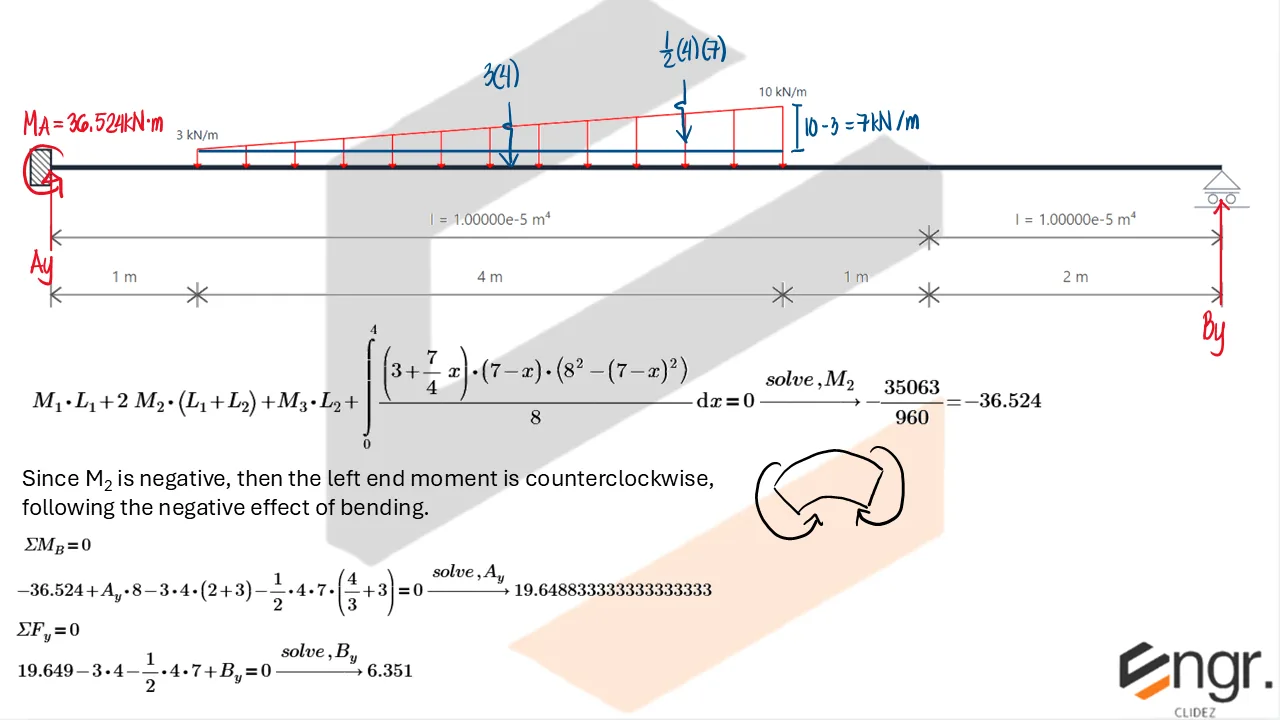
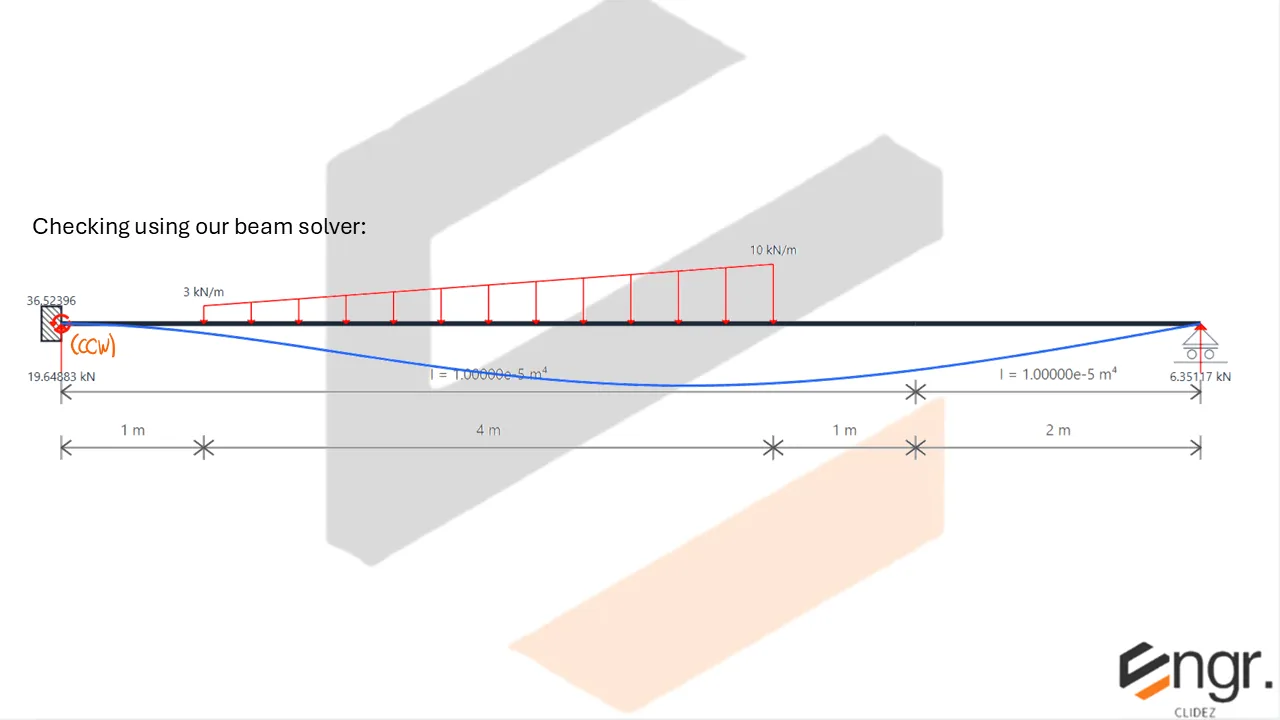
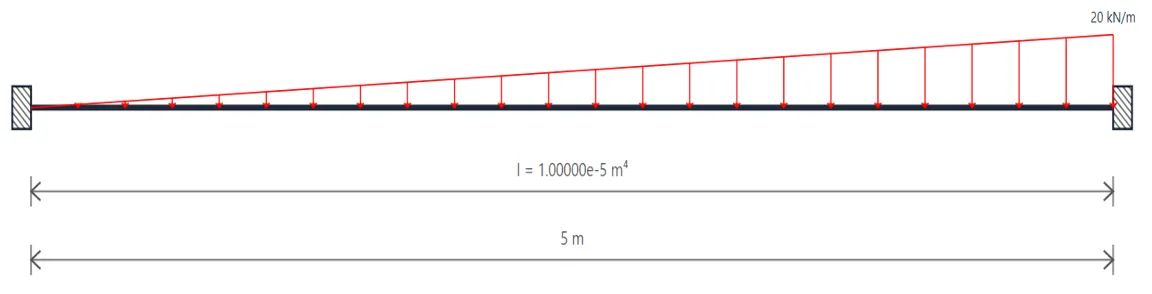
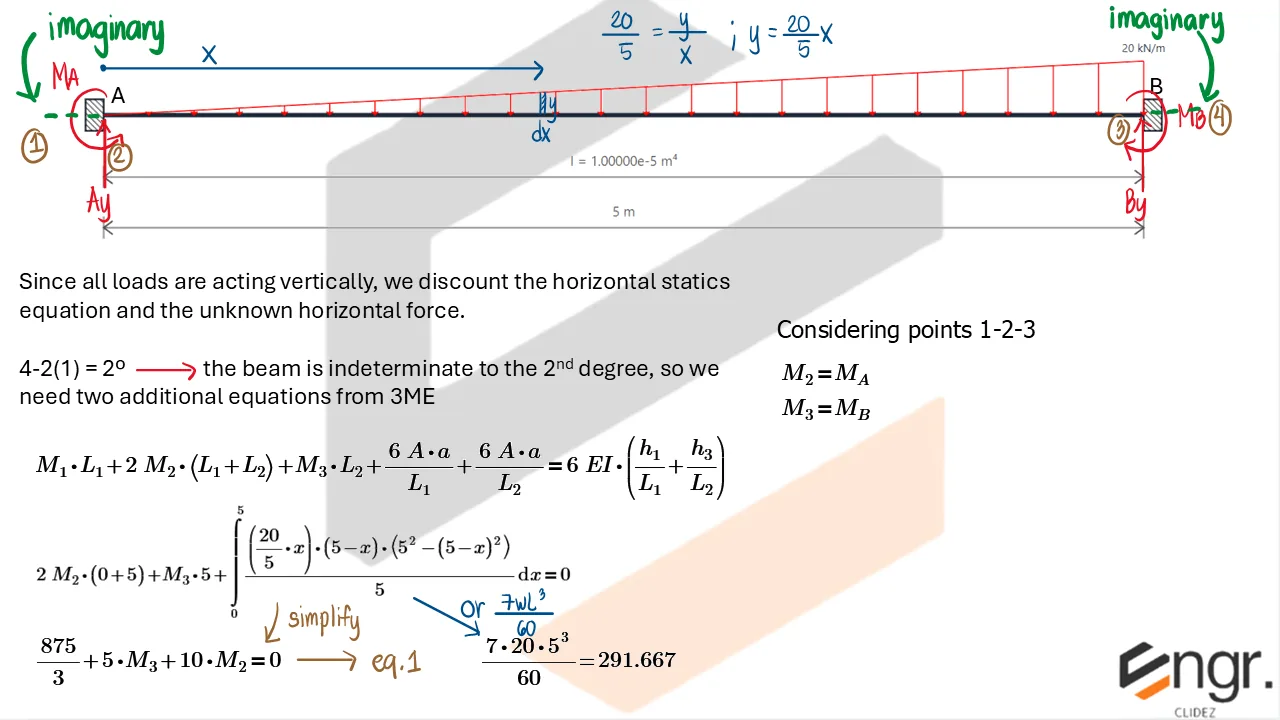
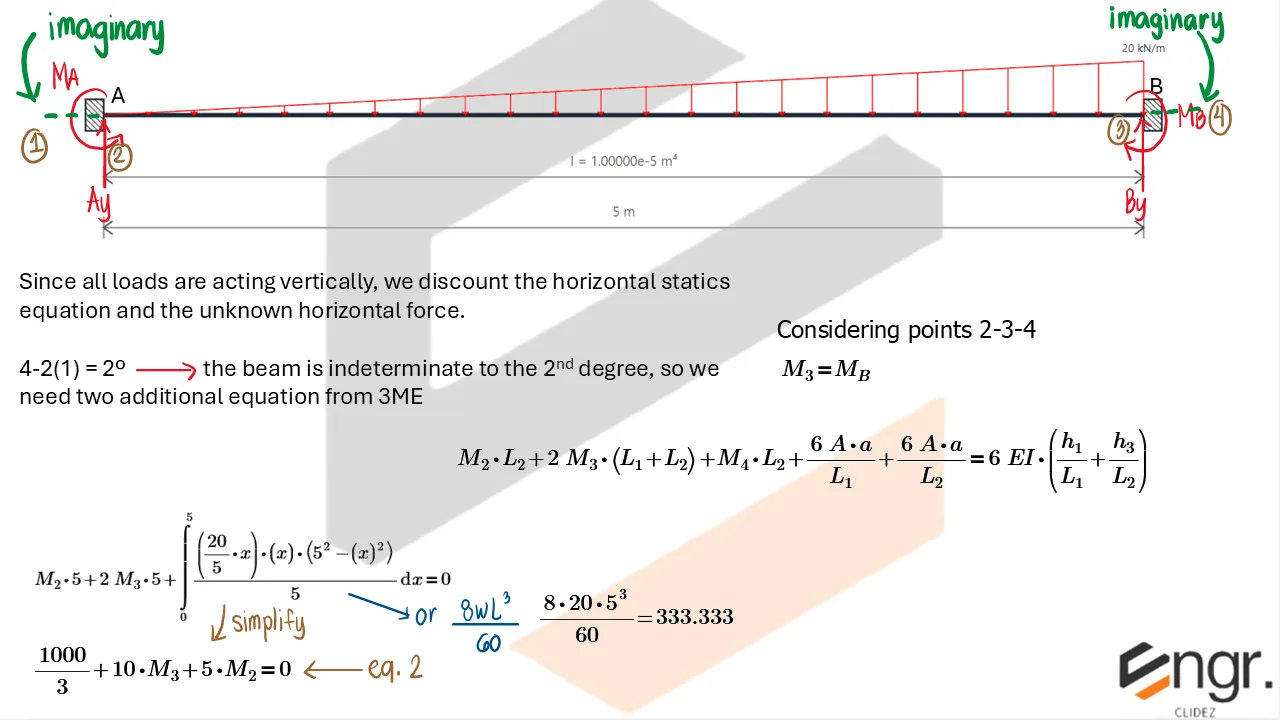
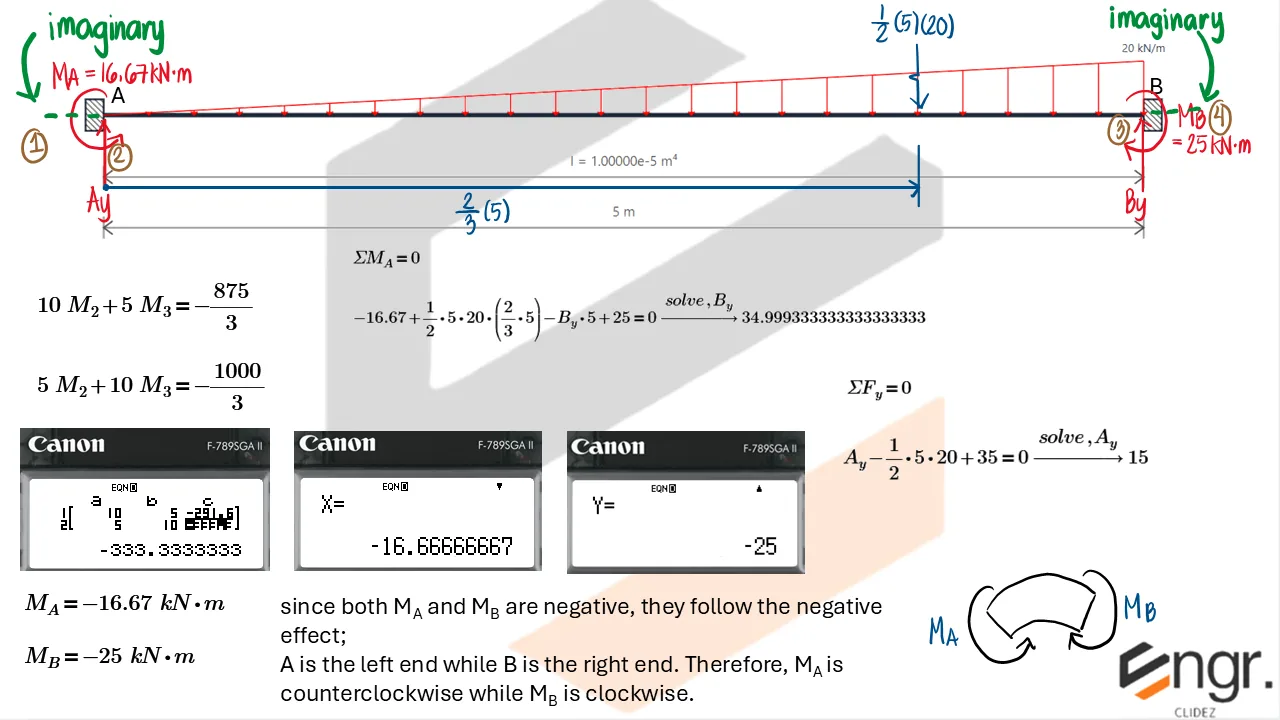
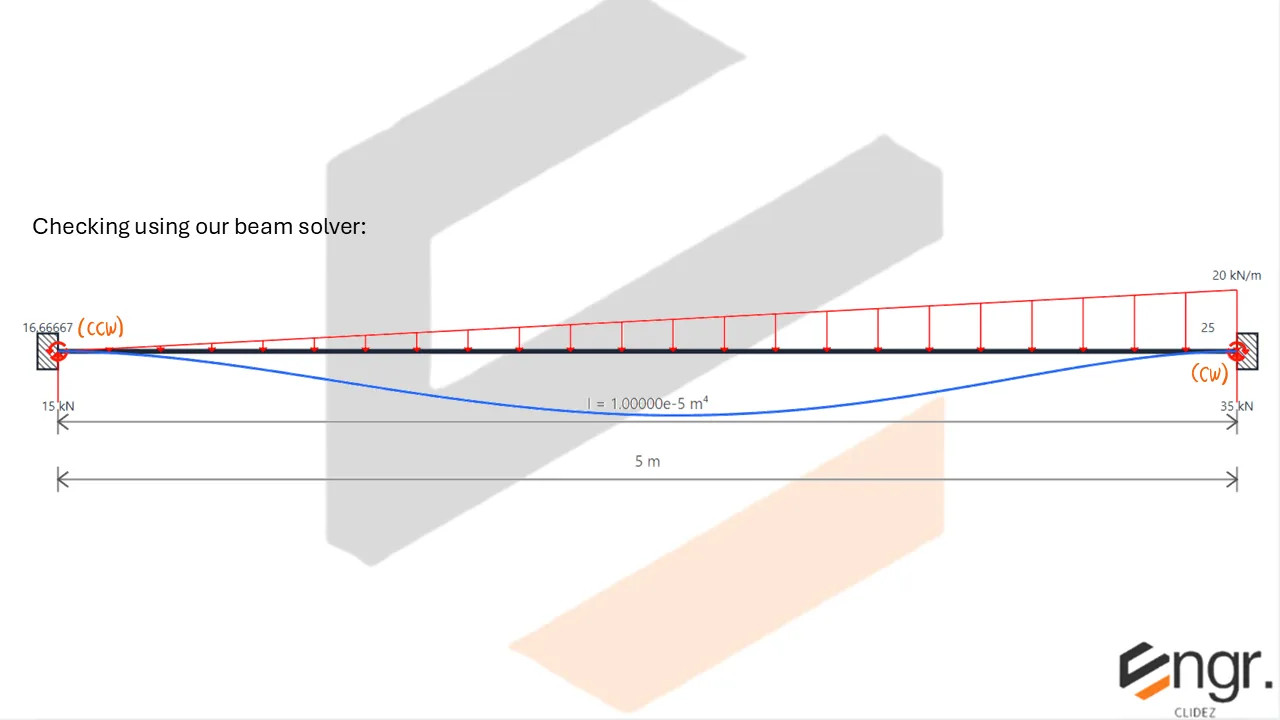
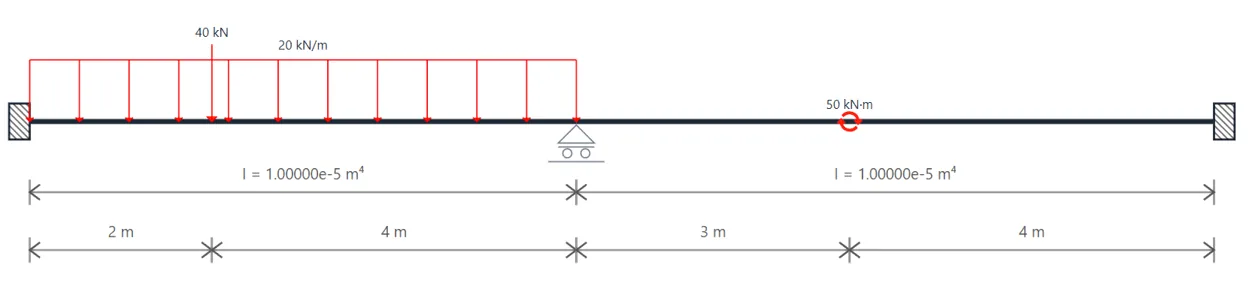
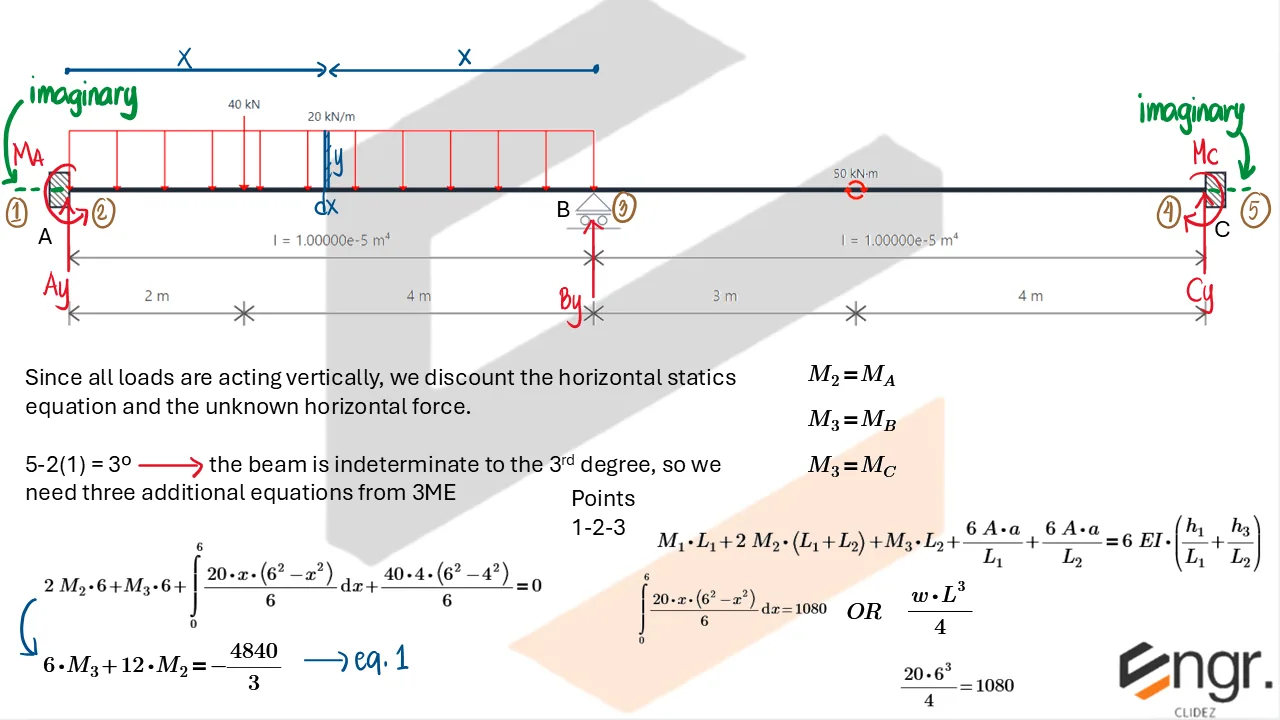
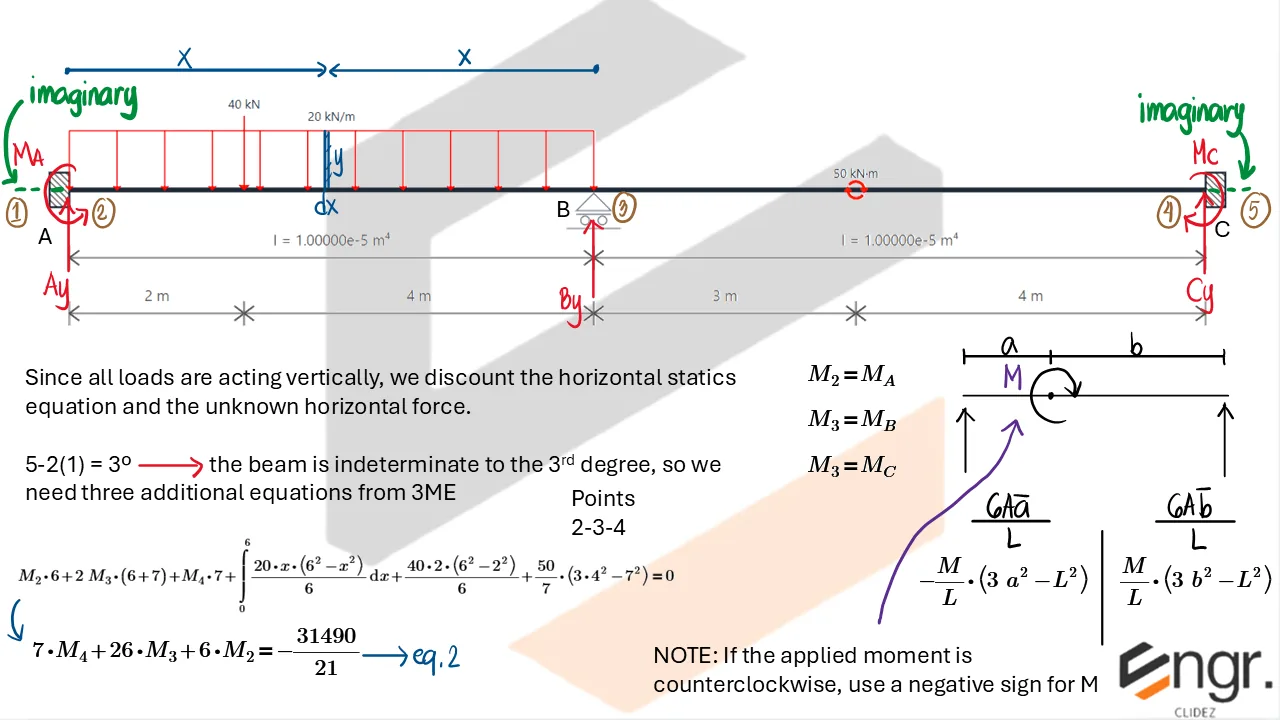
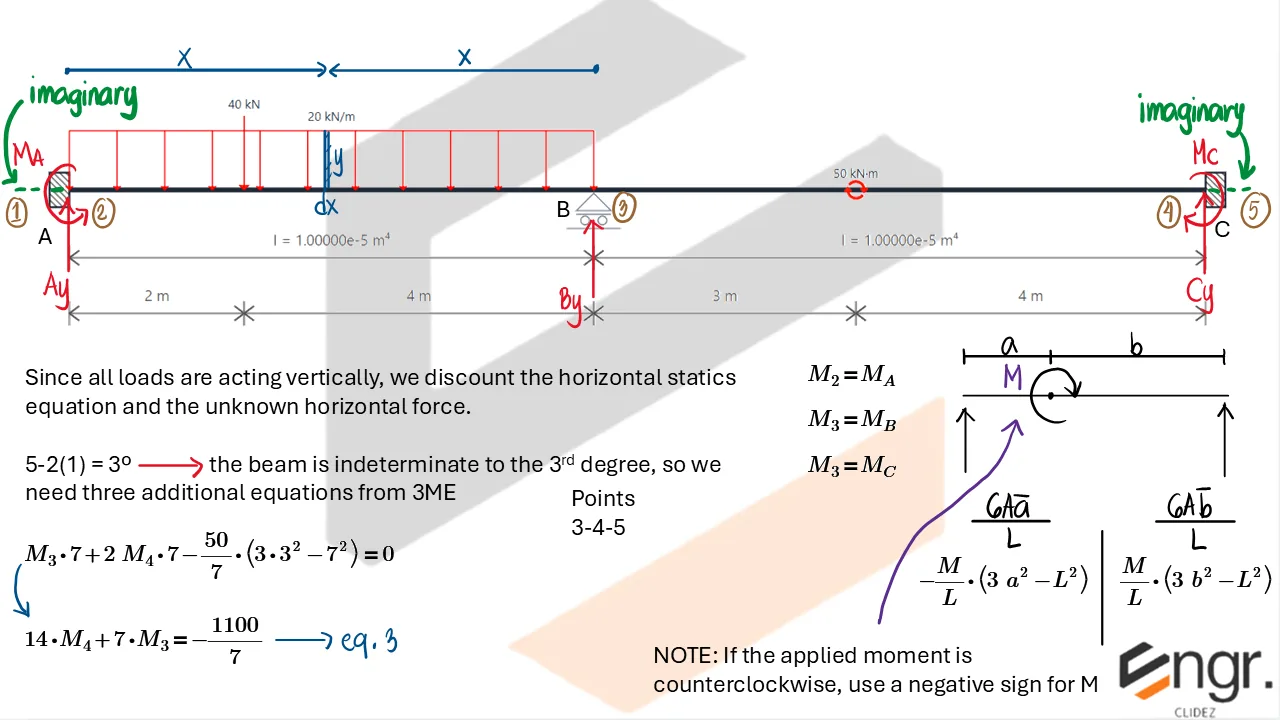
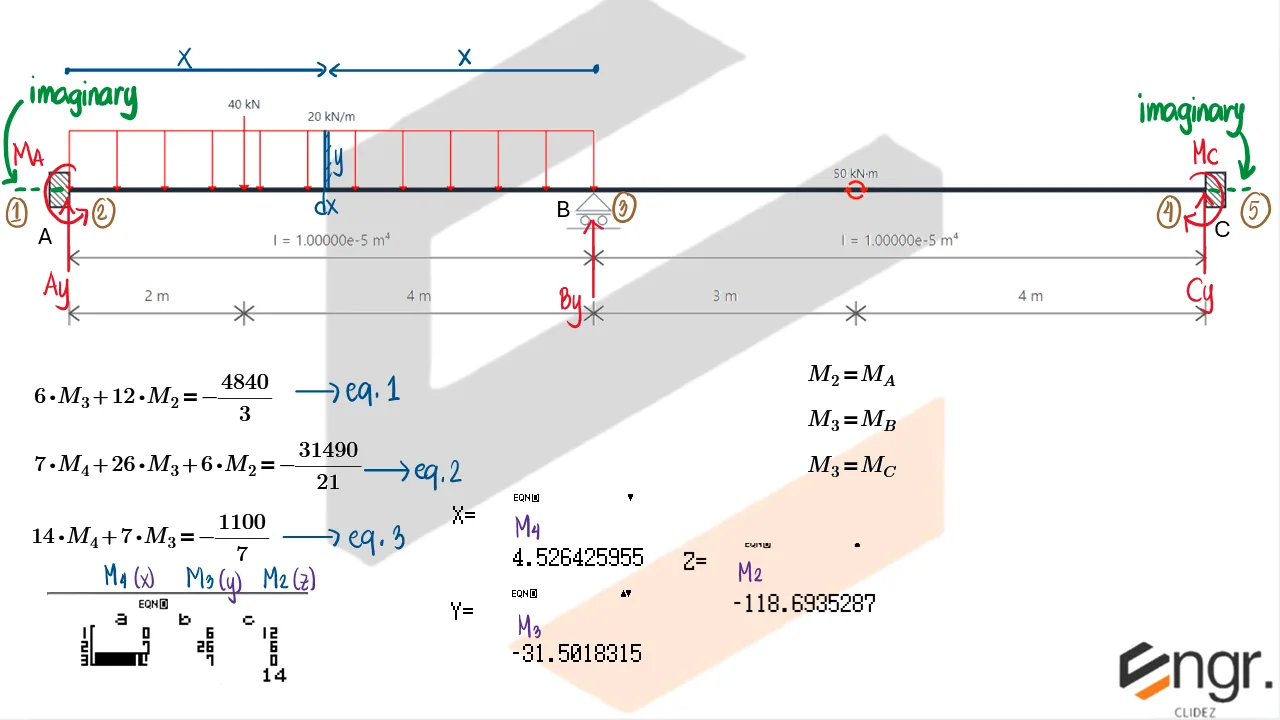
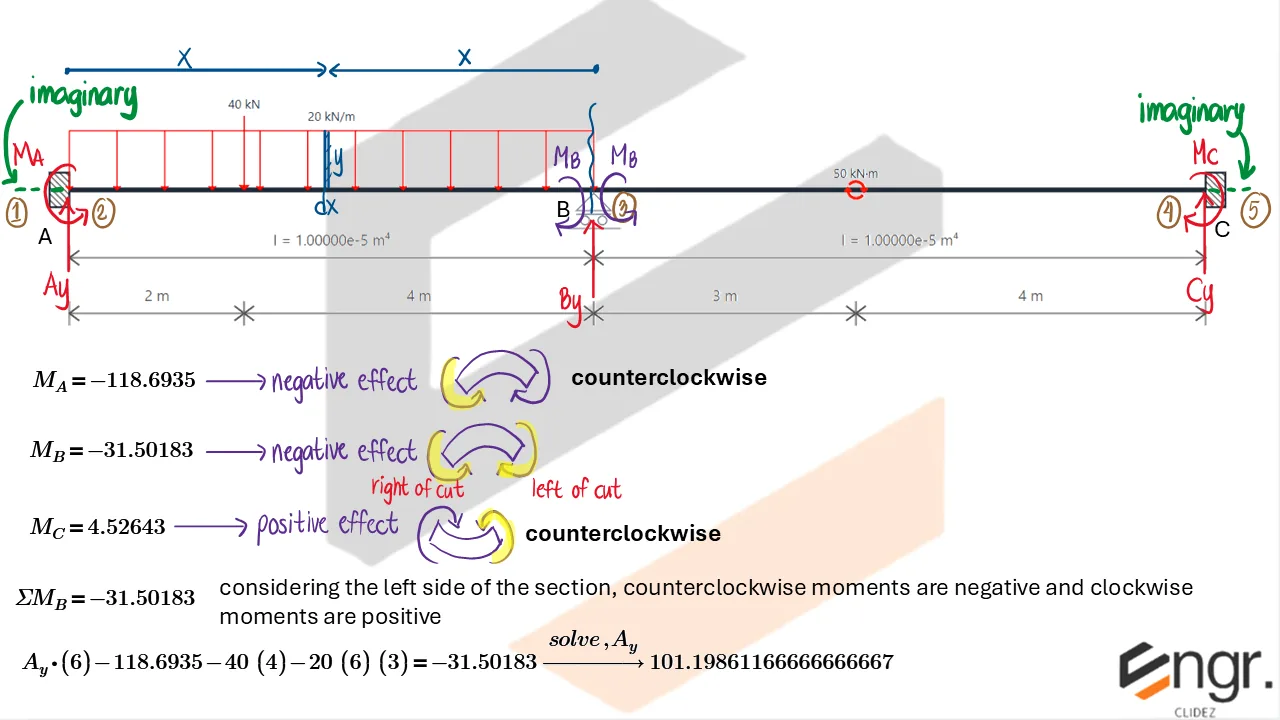
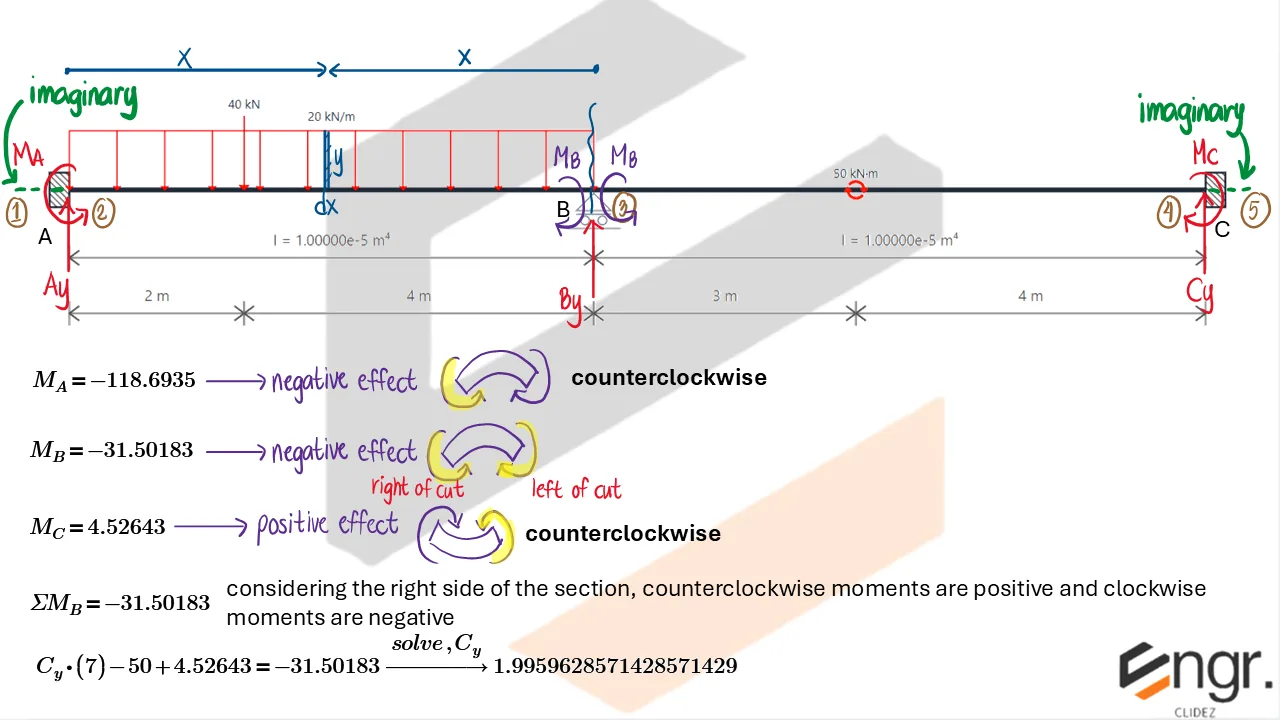
Indeterminate Beams
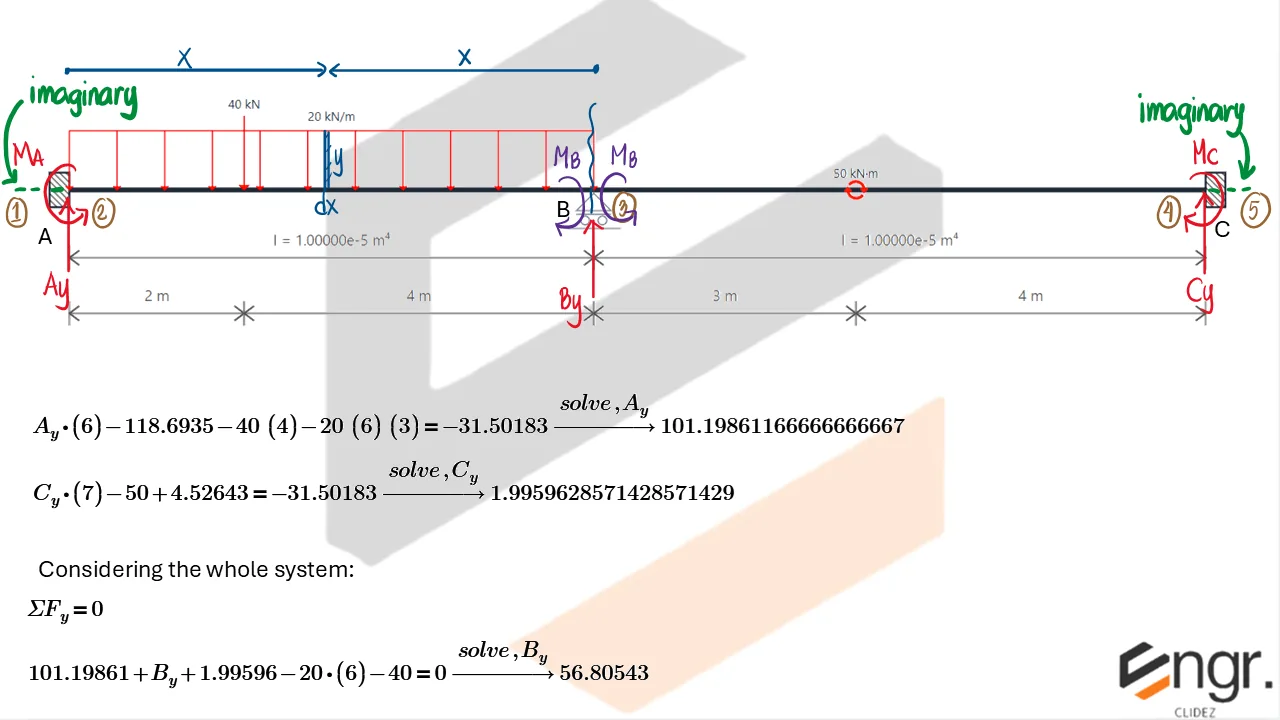
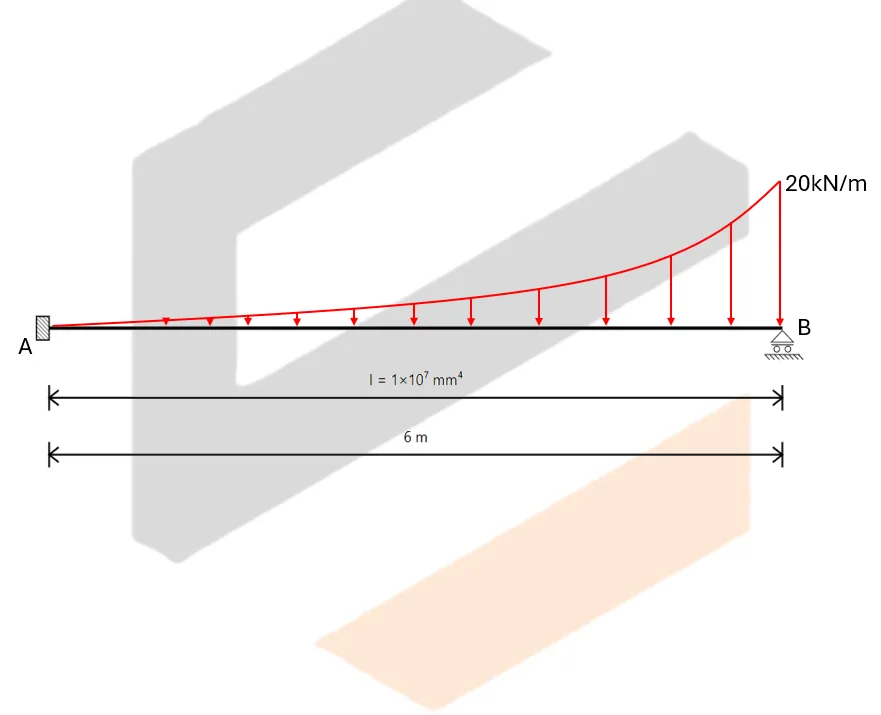
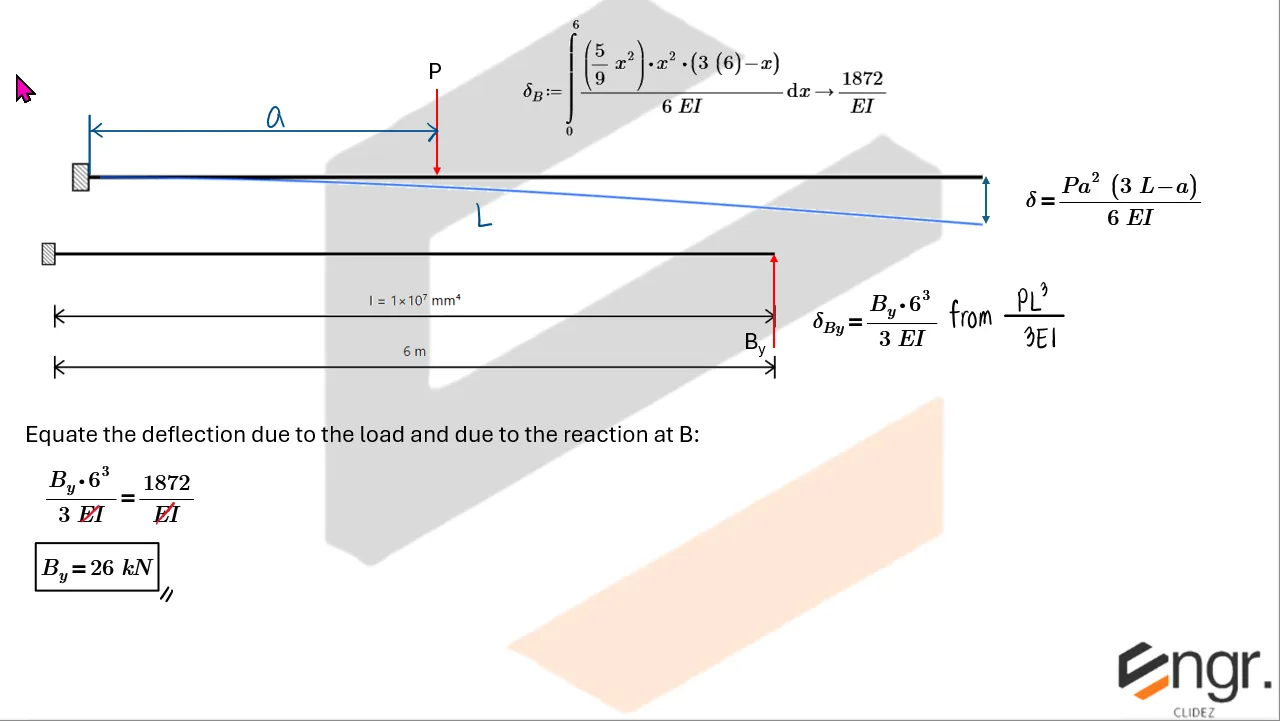
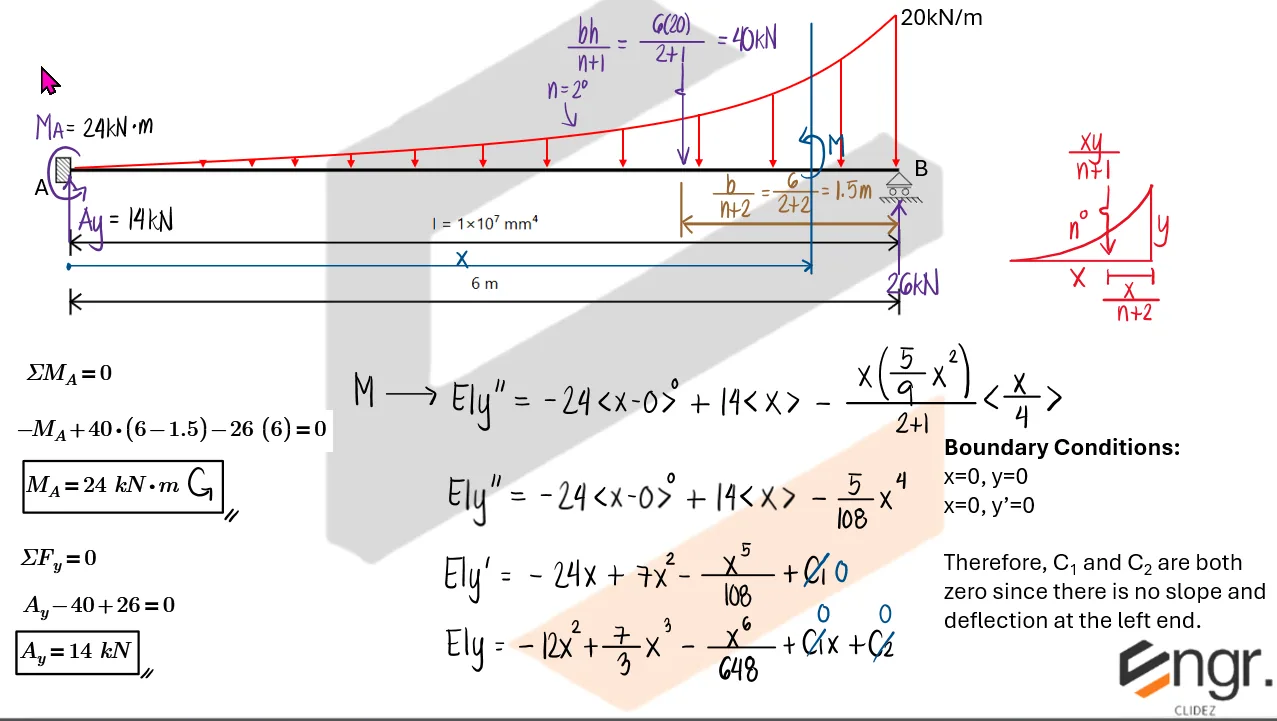
Unlike determinate beams, indeterminate beams have more unknown reactions than available static equilibrium equations. This means that while we still use methods like the Double Integration Method, Moment-Area Theorems, or the Conjugate Beam Method to compute slopes and deflections, additional compatibility conditions must be introduced to solve for the unknowns.
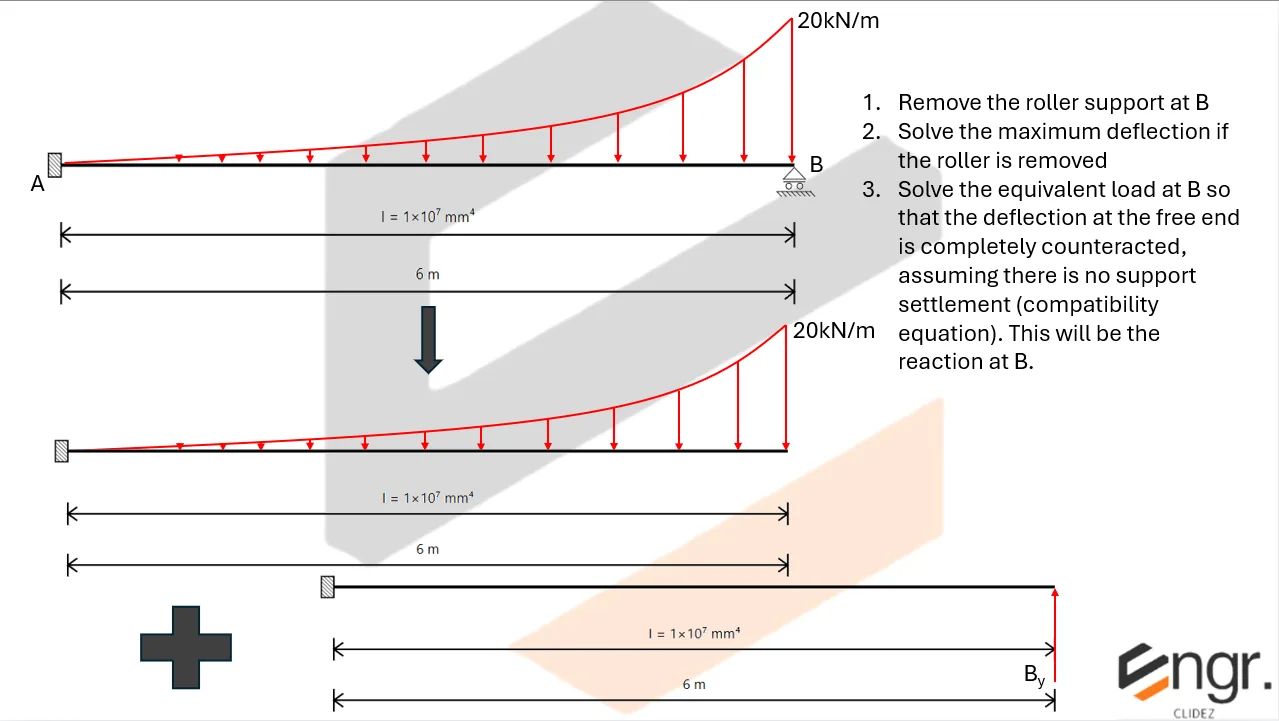
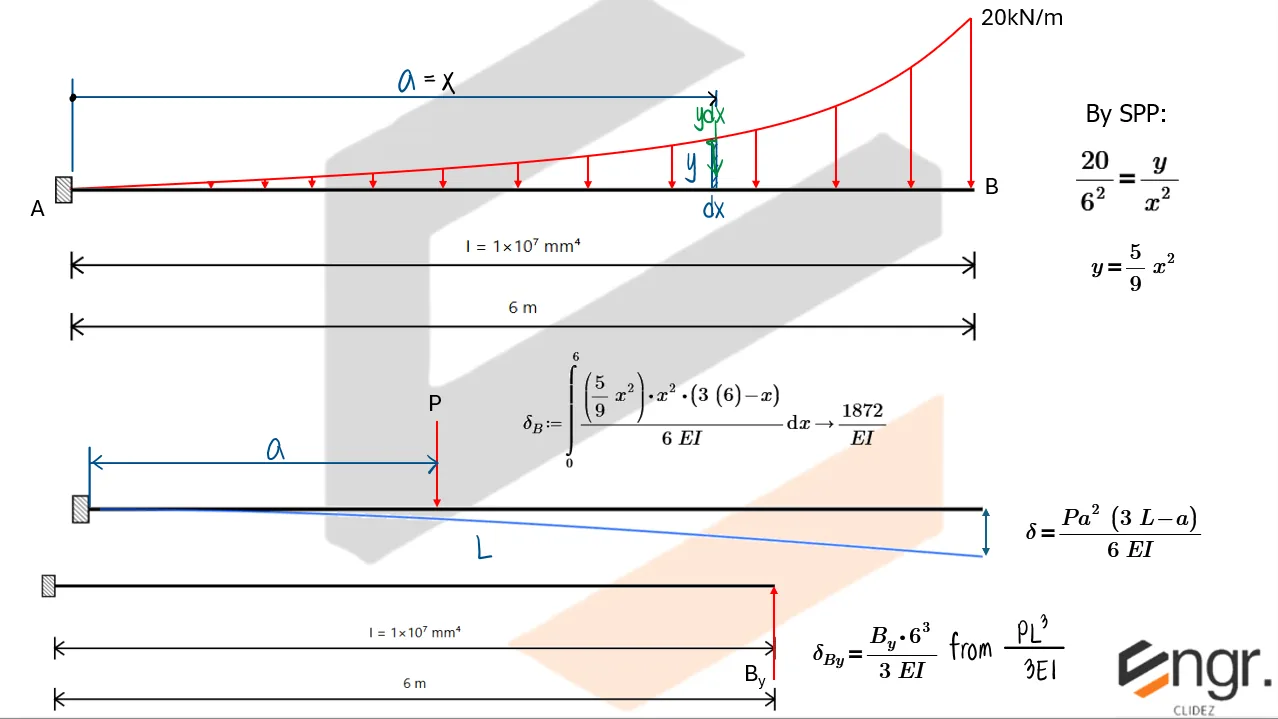
For example, if a beam has an extra support, we assume a redundant force (e.g., a reaction) and compute the resulting deflection at that point using superposition or virtual work. This deflection is then set equal to the required geometric constraint (usually zero), forming the compatibility equation.
The analysis then becomes a two-part process:
- Assume a redundant and analyze the structure using standard deflection techniques.
- Apply compatibility (e.g., total deflection at the redundant point must be zero) to solve for the redundant force.
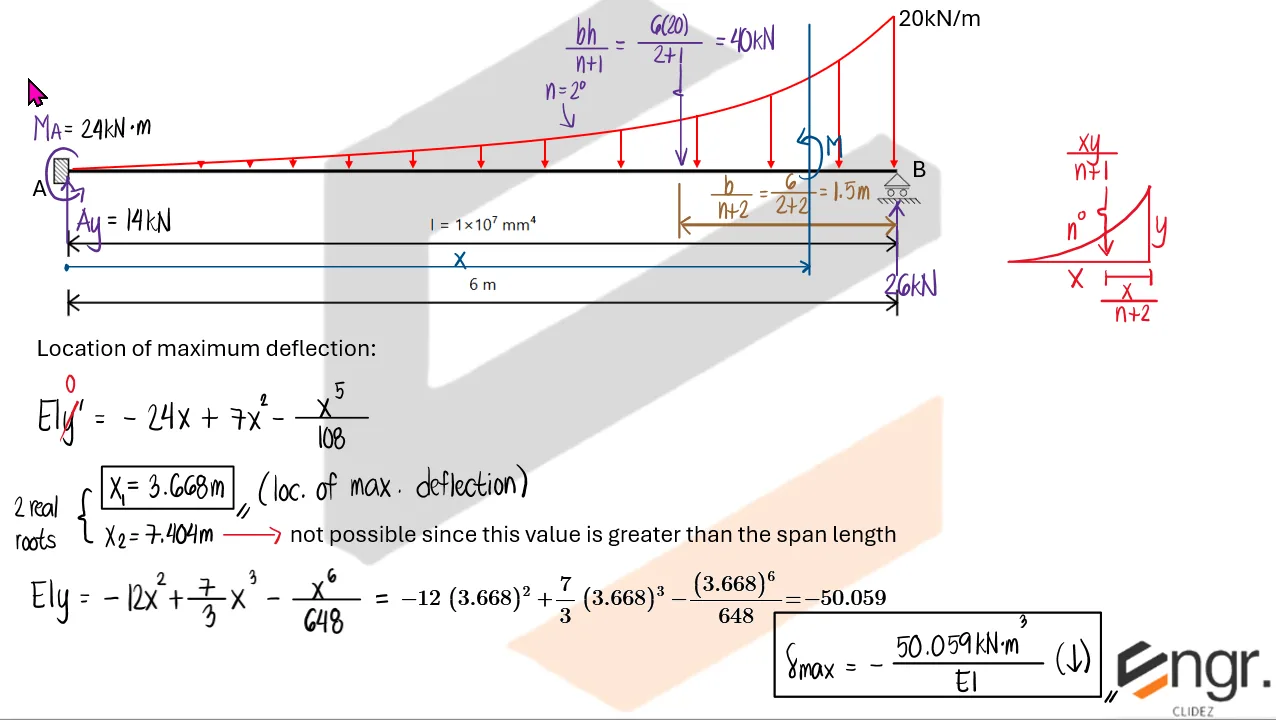
Once the redundant force is known, you can fully determine internal forces, reactions, and deflected shapes using the usual methods.