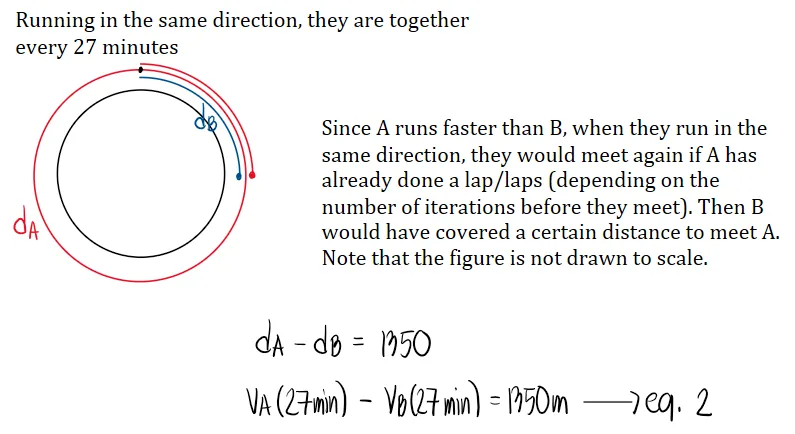
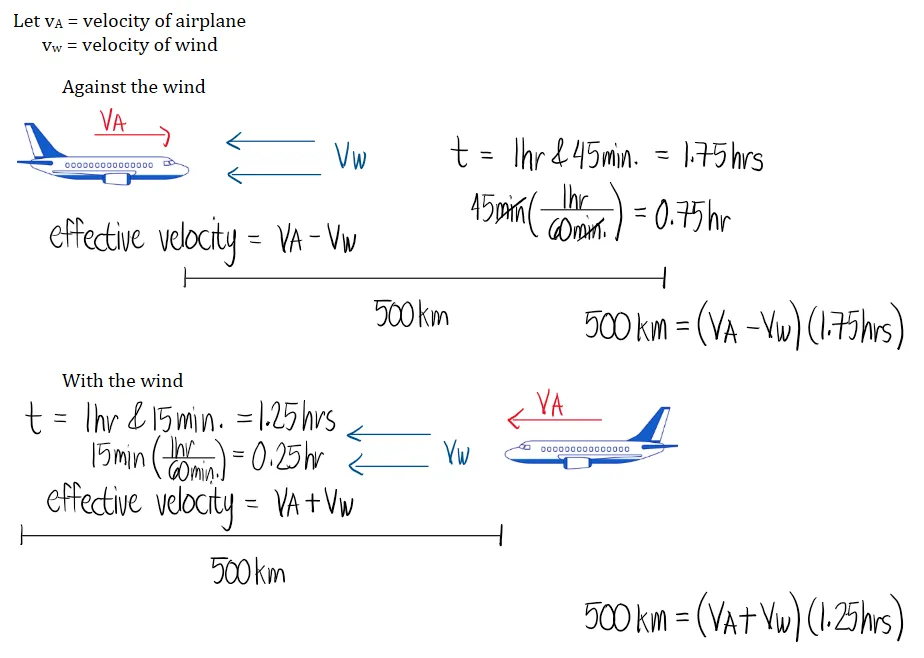
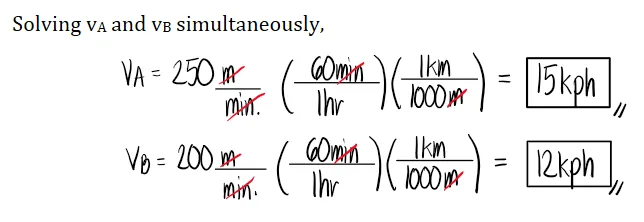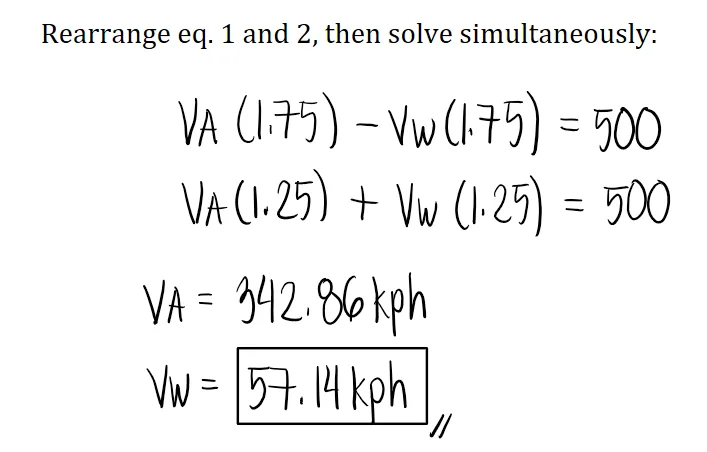Motion Problems
Motion problems involve objects moving at constant speed and use relationships between distance, rate (speed), and time.
Key Formula:
Variable Notation:
- $d$ → distance traveled (in km, m, etc.)
- $r$ → rate or speed (in km/hr, m/s, etc.)
- $t$ → time taken (in hours, minutes, etc.)
Common Motion Scenarios:
- Objects moving toward or away from each other
- Round trips or return journeys
- Chase problems (one faster object catching up)
Use the distance formula to write equations for each object or direction, then solve based on the relationship given in the problem.
Variable Speed
In problems involving rivers or flowing water, the motion of a boat or swimmer is affected by the speed of the current. The total effective speed depends on whether the motion is going with or against the current.
Key Relationships:
- With the current: The object moves faster.
- Against the current: The object moves slower.
Let the variables be:
- $r$ = rate of the boat or swimmer in still water
- $c$ = rate of the current
Effective Speeds:
- With the current:
- Against the current:
Once you know the effective rate, use the distance formula:
This type of problem often involves comparing times or distances for round trips or upstream/downstream travel.